信息学奥赛一本通T1448:深搜的剪枝技巧 电路维修
信息学奥赛一本通T1448:电路维修
【题目描述】
译自 BalticOI 2011 Day1 T3「Switch the Lamp On」
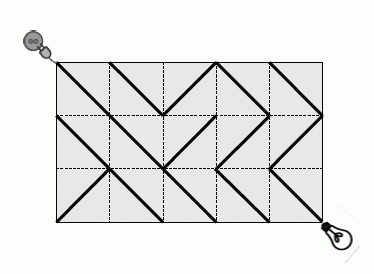
有一种正方形的电路元件,在它的两组相对顶点中,有一组会用导线连接起来,另一组则不会。
有 N×M 个这样的元件,你想将其排列成 N 行 M 列放在电路板上。电路板的左上角连接电源,右下角连接灯泡。
试求:至少要旋转多少个正方形元件才能让电源与灯泡连通,若无解则输出 NO SOLUTION。
【输入】
有多组测试数据。
第一行为测试数据组数,以下每组测试数据描述为:
第一行有两个整数 N 和 M。
在接下来的 N 行中,每行有 M 个字符。每个字符均为 "\" 或 "/",表示正方形元件上导线的连接方向。
【输出】
每组测试数据输出描述:
输出共一行,若有解则输出一个整数,表示至少要旋转多少个正方形元件才能让电源与灯泡连通;若无解则输出 NO SOLUTION。
【输入样例】
1
3 5
\\/\\
\\///
/\\\\【输出样例】
1
思路:
问题的关键在于思维的转换,首先,由于从左上到右下走的是对角线,因此,仅当 (n+m)%2==1 时无解,其他情况一定有解
首先进行建图,将格子的字符转为数字,即将 \ 转为 0,将 / 转为 1
然后考虑对角线格子的情况,无非以下四种:\\、\/、//、/\,同时,将这四种情况也转为数字的形式存储,相应的,行走的花费就为 0、1、0、1
再考虑所走的方向:左下、左上、右上、右下
此时,我们对图进行 BFS 搜索,考虑到两种状态:有花费、无花费,由于要使得花费最低,因此每次从队首出队时,我们要选一个无花费的元素出队,故而可利用双端队列 deque 进行优化:当有花费时,从队尾入队,当无花费时,从队首入队,从而保证队列的两端性与单调性
此时只剩下一个问题,就是最小花费的问题,即什么情况下才能将元素入队,我们可以借助一个数组,存储之前的花费,当某一步的花费较之前的花费缩小时,即将元素入队
【源程序】
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#include<bitset>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define LL long long
#define Pair pair<int,int>
LL quickPow(LL a,LL b){ LL res=1; while(b){if(b&1)res*=a; a*=a; b>>=1;} return res; }
LL multMod(LL a,LL b,LL mod){ a%=mod; b%=mod; LL res=0; while(b){if(b&1)res=(res+a)%mod; a=(a<<=1)%mod; b>>=1; } return res%mod;}
LL quickMultPowMod(LL a, LL b,LL mod){ LL res=1,k=a; while(b){if((b&1))res=multMod(res,k,mod)%mod; k=multMod(k,k,mod)%mod; b>>=1;} return res%mod;}
LL quickPowMod(LL a,LL b,LL mod){ LL res=1; while(b){if(b&1)res=(a*res)%mod; a=(a*a)%mod; b>>=1; } return res; }
LL getInv(LL a,LL mod){ return quickPowMod(a,mod-2,mod); }
LL GCD(LL x,LL y){ return !y?x:GCD(y,x%y); }
LL LCM(LL x,LL y){ return x/GCD(x,y)*y; }
const double EPS = 1E-6;
const int MOD = 1000000000+7;
const int N = 1000+5;
const int dx[] = {0,0,-1,1,1,-1,1,1};
const int dy[] = {1,-1,0,0,-1,1,-1,1};
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int x, y;
int step;
Node() {}
Node(int x, int y, int step) : x(x), y(y), step(step) {}
};
int n, m;
int G[N][N]; //将格子的字符转为数字 0:\ 1:/
int dirG[4][2] = {{0, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 1}, {1, 0}}; /* 对角线格子的情况:\\,\/,//,/\ */
int disG[4] = {0, 1, 0, 1}; //对角线格子相应的状态下是否能走
int dir[4][2] = {{-1, -1}, {-1, 1}, {1, 1}, {1, -1}}; //走对角线的方向:左下,左上,右上,右下
int dis[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
void BFS() {
deque<Node> Q;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
memset(dis, INF, sizeof(dis));
Q.push_front((Node){0, 0, 0});
while (!Q.empty()) {
Node node = Q.front();
Q.pop_front();
int x = node.x, y = node.y;
int step = node.step;
if (vis[x][y])
continue;
vis[x][y] = true;
if (x == n && y == m) {
printf("%d\n", step);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int gx = x + dirG[i][0];
int gy = y + dirG[i][1];
if (gx < 0 || gy < 0 || gx > n || gy > m)
continue;
int nx = x + dir[i][0];
int ny = y + dir[i][1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx > n || ny > m)
continue;
if (dis[nx][ny] == INF) {
if (G[gx][gy] != disG[i]) {
Q.push_back(Node(nx, ny, step + 1));
dis[nx][ny] = step + 1;
}
else {
Q.push_front(Node(nx, ny, step));
dis[nx][ny] = step;
}
}
else if (G[gx][gy] == disG[i] && step < dis[nx][ny])
Q.push_front(Node(nx, ny, step));
}
}
}
int main() {
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
char c = getchar();
while (c != '\\' && c != '/')
c = getchar();
if (c == '\\')
G[i][j] = 0;
else
G[i][j] = 1;
}
}
if ((n + m) % 2)
printf("NO SOLUTION\n");
else
BFS();
}
return 0;
}
信息学奥赛一本通T1448:深搜的剪枝技巧 电路维修 归属于 深搜的剪枝技巧,更多同类题解源程序见:深搜的剪枝技巧 和 电路维修
- 发表于 2020-05-21 10:20
- 阅读 ( 1266 )
- 分类:信息学奥赛一本通
你可能感兴趣的文章
- 信息学奥赛一本通T1454:深搜的剪枝技巧 山峰和山谷 1940 浏览
- 信息学奥赛一本通T1452:深搜的剪枝技巧 Keyboarding 1311 浏览
- 信息学奥赛一本通T1453:深搜的剪枝技巧 移动玩具 1168 浏览
- 信息学奥赛一本通T1451:深搜的剪枝技巧 棋盘游戏 1358 浏览
- 信息学奥赛一本通T1450:深搜的剪枝技巧 Knight Moves 1430 浏览
- 信息学奥赛一本通T1449:深搜的剪枝技巧 魔板 1009 浏览
相关问题
0 条评论
0 篇文章
作家榜 »
-
 admin
2 文章
admin
2 文章
-
 张芳
0 文章
张芳
0 文章
-
 hanna
0 文章
hanna
0 文章
-
 Jason
0 文章
Jason
0 文章
-
 lixiaioqian
0 文章
lixiaioqian
0 文章
-
 GeraldWrora
0 文章
GeraldWrora
0 文章
-
 董伟
0 文章
董伟
0 文章
-
 信奥达人
0 文章
信奥达人
0 文章